dtSearch Quick Start
Article: dts0160
See also:
Welcome/Introduction: dtSearch Desktop/Network
Installing dtSearch on a network
How dtSearch works and indexing tips
Optimizing indexing of large document collections
To get started with dtSearch, the first step is to build an index of your documents. Once the index is built, dtSearch can use it to search your documents quickly.
Indexing Documents
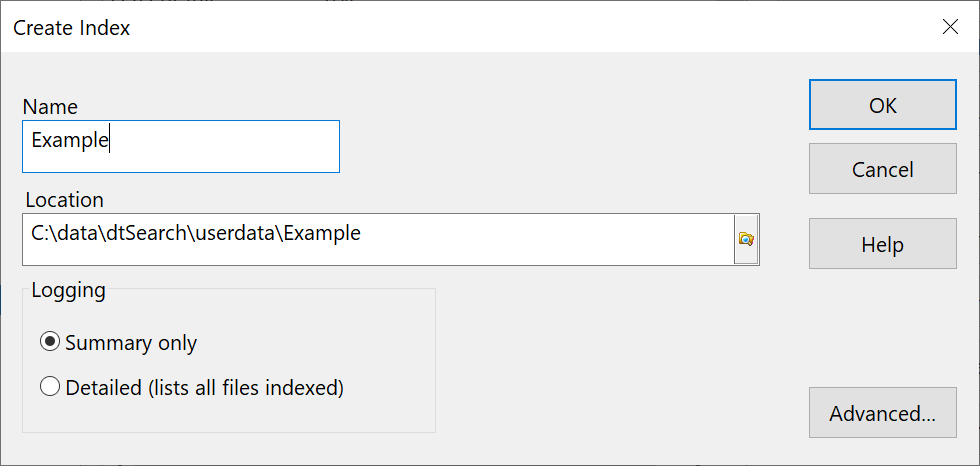
1. Choose Create Index from the Index menu.
2. In the Create index dialog box, enter a name for the index and click OK.
3. dtSearch will ask if you want to add documents to the index. Click Yes to go to the Update Index dialog box.
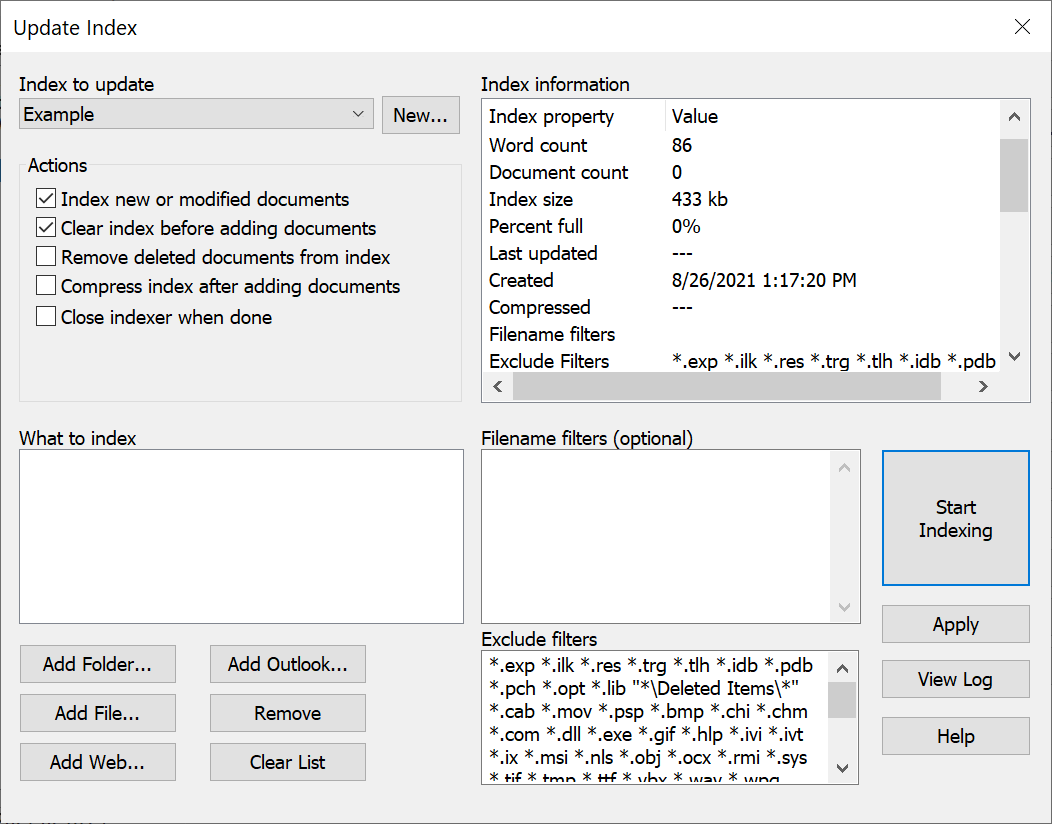
4. Click Add folder... to add a folder to the list of folders to index.
5. Click Add web... to index a site using the dtSearch Spider.
6. Click Start Indexing to begin adding documents to your index.
dtSearch automatically recognizes popular file types. For a complete list of the file formats that dtSearch supports, see Supported File Types.
Searching using the Index
1. Click the Search button on the dtSearch button bar, or press Ctrl-S, to open the Search dialog box.
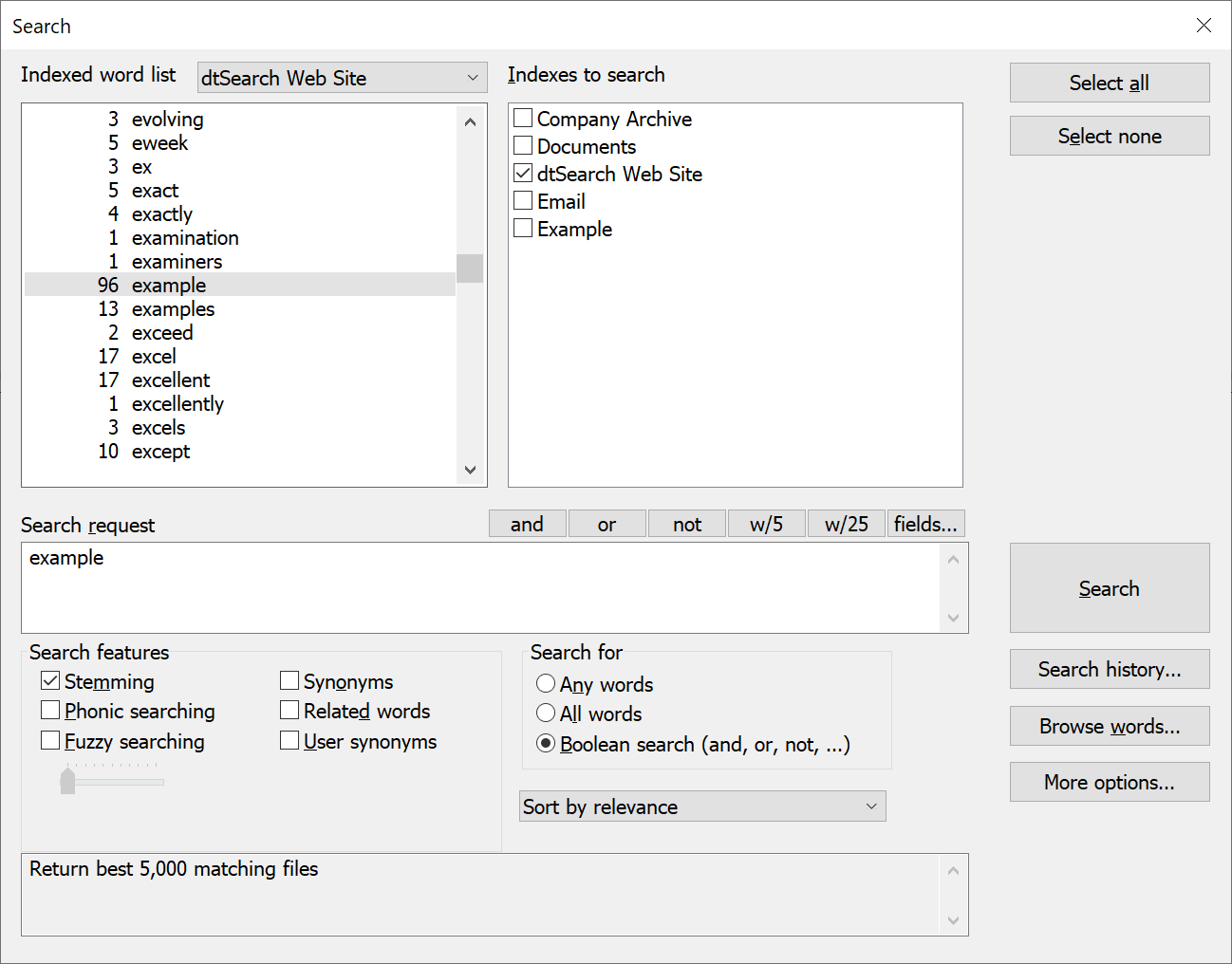
Indexes to search
The top right of the dialog box shows a list of the indexes you have created; select one or more to search.
Indexed word list
The top left of the dialog box shows a list of the words in the currently selected index. If more than one index is selected for searching, you can select the index to display in the word list by clicking the down arrow above the word list.
2. Enter a search under Search Request.
3. Select any items under Search features (such as fuzzy searching) that you want to use.
4. Click Search to begin the search.
Search Types
Any words: use quotation marks around phrases, put + (plus) in front of any word or phrase that is required, and - (minus) in front of a word or phrase to exclude it. Examples:
banana pear "apple pie"
"apple pie" -salad +"ice cream"
All words: like an "any words" search except that all of the words in the search request must be present for a document to be retrieved.
Boolean search: a group of words, phrases, or macros linked by connectors such as AND and OR that indicate the relationship between them. Examples:
|
Search Request |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
apple and pear |
both words must be present |
|
apple or pear |
either word can be present |
|
apple w/5 pear |
apple must occur within 5 words of pear |
|
apple not w/5 pear |
apple must occur, but not within 5 words of pear |
|
apple and not pear |
only apple must be present |
|
name contains smith |
the field name must contain smith |
|
apple w/5 xfirstword |
apple must occur in the first five words |
|
apple w/5 xlastword |
apple must occur in the last five words |
If you use more than one connector, use parentheses to indicate precisely what you want to search for. For example, apple and pear or orange juice could mean (apple and pear) or orange, or it could mean apple and (pear or orange).
You can use variable term weighting in a search request to weigh some words more heavily than others in ranking search results. Example: apple:5 and pear:3
See dtSearch search syntax for more search operators.
Search Features
Stemming searches other grammatical forms of the words in your search request. For example, with stemming enabled a search for applies would also find apply, applying or applied.
Phonic searching finds words that sound similar to words in your request, like Smith and Smythe.
Fuzzy searching sifts through scanning and typographical errors. Fuzziness adjusts from 1 to 10 depending on the degree of misspellings. A search for alphabet with a fuzziness of 1 would find alphaqet; with a fuzziness of 4, it would find both alphaqet and alpkaqet.
Synonym searching tells dtSearch to use a thesaurus to automatically expand a search to include synonyms or related concepts, including three optional levels.
To see how stemming, phonic searching, fuzzy searching or wildcards will affect your search, click the Browse Words button.
To browse the thesaurus used for synonym searching, click the Thesaurus... button.
Click the Fields button for a list of searchable fields, if you want to limit your search to a particular field.
To search without an index, or to search by filename, date, or size, click the More search options tab.
Viewing Search Results
After a search, dtSearch will display the results of the search. The top half of the dtSearch window will list all of the files retrieved in the search, and the lower half will show the first document in the list, with hits highlighted in yellow. To see hits highlighted in multiple colors, click Options > Preferences > Fonts and Colors and check the "Multiple colors" box.
For PDF files, you can download a separate hit-highlighting plug-in to enable dtSearch to display PDF files in Adobe Reader with hits highlighted.
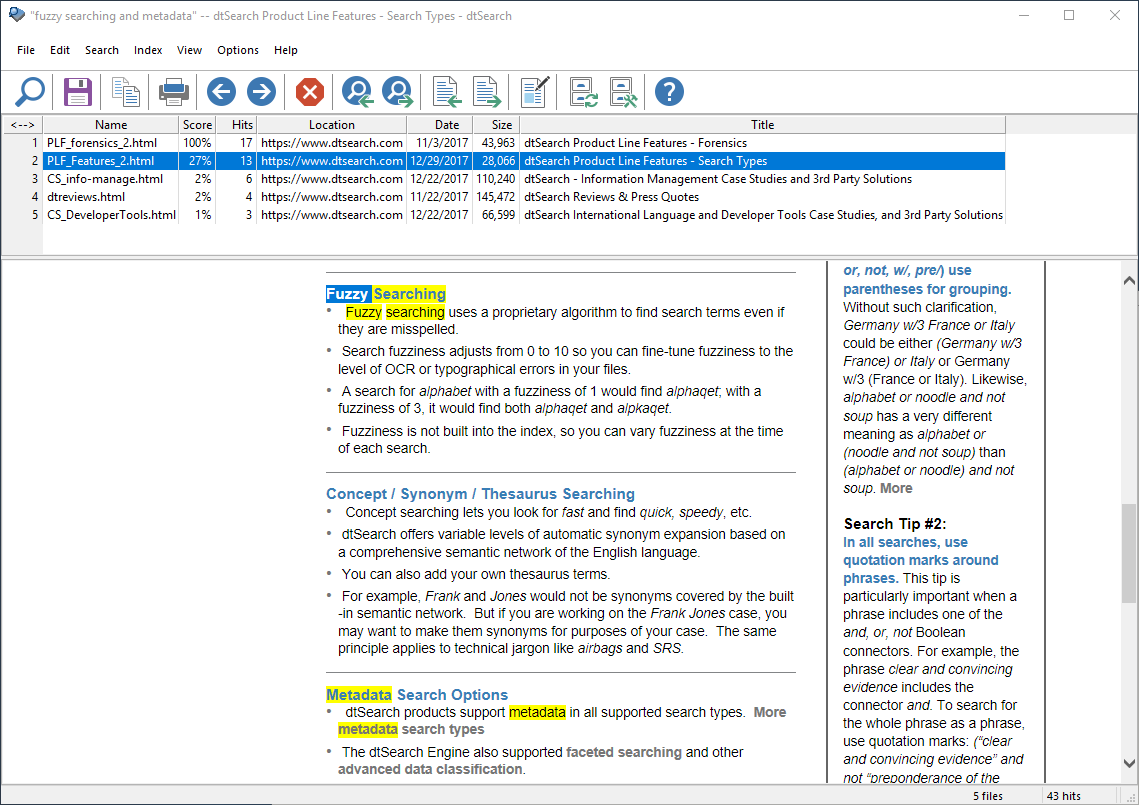
1. To select a document to view from the search results list, double-click on it.
2. To jump to the next hit in a document window, click Next Hit  on the button bar (or press SPACEBAR). Press Ctrl-SPACEBAR, or click the Next Doc
on the button bar (or press SPACEBAR). Press Ctrl-SPACEBAR, or click the Next Doc  button, to go to the next document.
button, to go to the next document.
3. To change the way search results are sorted, click on one of the column headers (Name, Score, Location, Date, etc.).
4. Click the Launch  button to open a document in the application associated with it. For example, a Word document would be launched in Microsoft Word.
button to open a document in the application associated with it. For example, a Word document would be launched in Microsoft Word.
To view or reuse a prior search request, click the Search History tab in the Search dialog box.
Create a Quick Summary of Your Search Results
An easy way to see all hits in all retrieved documents is to build a search report. A search report shows all hits along with the amount of context that you request.
1. Choose Search Report from the Search menu. The Generate Search Report dialog box will appear.
2. Enter the number of words (or paragraphs) of context that you want dtSearch to include in your search report and click OK to generate the report.
3. The search report will open in your word processor so you can edit or print it
Updating an Index
If you edit or add to your documents, you will need to update your index to reflect the changes.
To update your index, choose Update Index in the Index menu (or press Ctrl-U). Check the Index new or modified documents box and the Remove deleted documents box, and then click the Start Indexing button. To optimize an index that has been updated many times, select the Compress index option.
To schedule automatic index updates, click Index > Index Manager and click the Schedule Updates.